
A visionary multi-user platform model for protecting consumer privacy and meeting grid needs.
Tanya conceived of LEEP on behalf of PECI to bridge the needs of consumers and utilities. More of the grid is powered by intermittent, renewable generating resources. Grid infrastructure is not equipped to accommodate these new technologies – creating challenges for future clean energy affordability and equity.
In response to consumer choice, disruptive technologies, and regulatory pressure, many load-serving entities are looking to: develop portfolios of flexible grid resources that can balance fluctuations in demand and renewable generation; enhance system resiliency by diversifying grid assets; increase system efficiency through more dynamic pricing models; and reduce reserve requirements through demand reduction and load shaping.

While battery energy storage and microgrids are exciting areas of research, they alone will not optimize the largest drivers of the need for grid flexibility – renewable energy production and residential building loads. Technological advances have made building-to-grid energy management a viable, elegant, and attractive option to address the uncertainty of fluctuating, renewable power supply by harnessing the vast sea of latent demand flexibility inherent in the way consumers currently interact with sub-metered loads.
A modern grid must leverage these advances in metering, sensing, and control, to include autonomous demand-side management (DSM) as a critical component within a balanced and diverse portfolio of grid assets.
For the technical side of building a functional US LEEP platform, Tanya assembled The Local Energy Exchange Platform (LEEP) research consortium with PECI, The City and School District of Tenino, Washington State University, the Pacific Northwest National Lab and a strategic advisory group of community and investor owned utilities. The technical portion of the project builds upon previous work to expand DSM technology that currently exists at U.S. Department of Energy (USDOE) TRL5 overall (component/process validation in relevant environment) to a TRL of 7-8.
Through LEEP’s initial research, development, and field trials, the gateway/controller will enable rapid response to evolving complexity in power supply, markets, and pricing without creating an undue burden on utilities or consumers.
LEEP aggregates, at utility scale, controllable energy assets within homes and businesses to demonstrate evolving grid use cases as the grid and markets evolve.
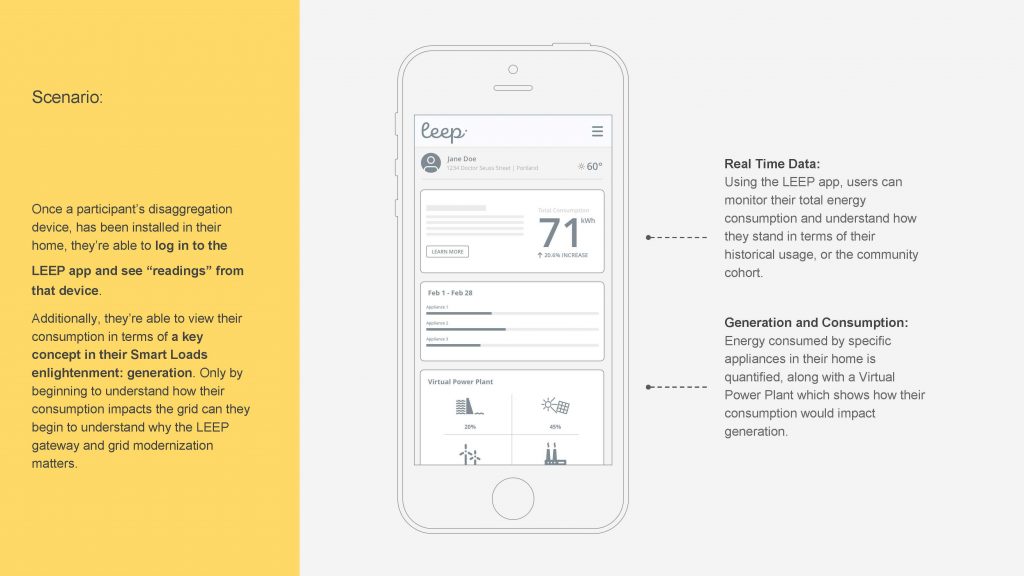
LEEP’s aggregation platform allows utilities and aggregators to place real-time pricing, control, and resource requests (e.g. reactive power, voltage control, energy arbitrage). LEEP’s gateway then matches backend inputs with a consumer-facing frontend that controls sub-metered loads. The gateway will learn, estimate, orchestrate, and aggregate energy flexibility from individual user assets and devices to deliver whole-home flexibility to the grid without requiring substantial management from utilities, aggregators, or users.
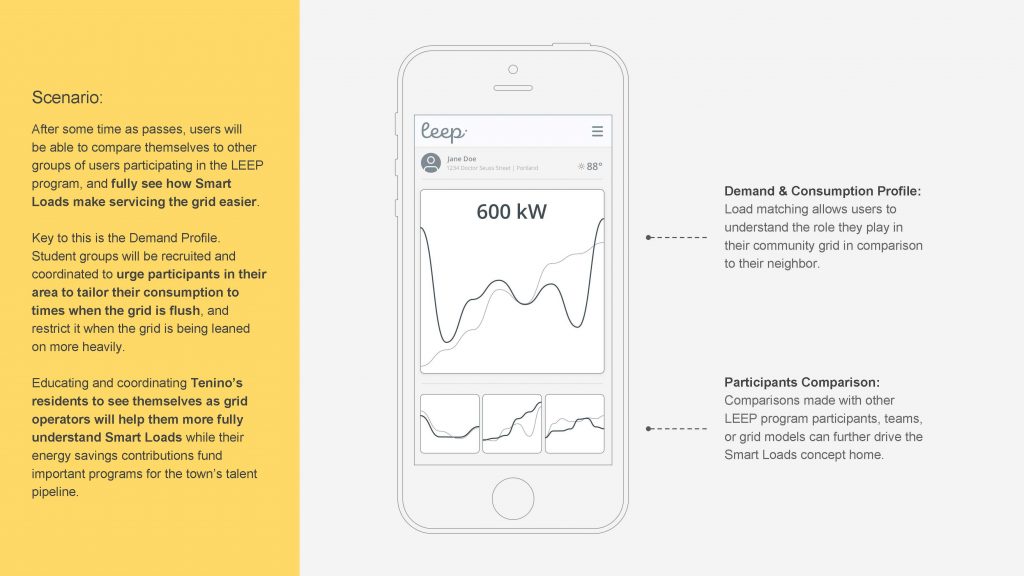
On the consumer side of the equation, LEEP seeks to protect user privacy, increase user comfort and provide a social and educational interface that is more motivating to individual participants than single home energy savings or incentives alone. The program seeks to intuitively help users understand the need for loads to begin following generation and create a market value for smart devices through a better understanding of the environmental imperative for such flexibility.
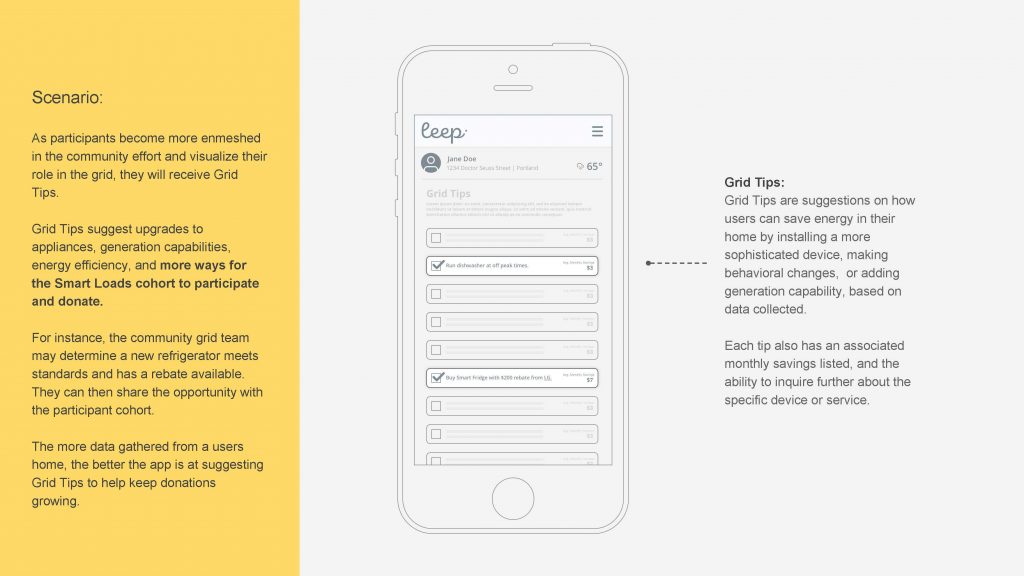
LEEP’s interface and program design therefore allows users with little understanding of or interest in complex utility needs to aggregate and transact both individual device and whole-home flexibility. Community members will opt in their connected assets via the user interface in order to pool the flexibility of their assets with other residents and, eventually, will be able to donate any estimated economic benefits (for example, efficiency savings, incentives, carbon offsets, or renewable energy certificates) to their local schools or other lower income residents who cannot afford such devices.
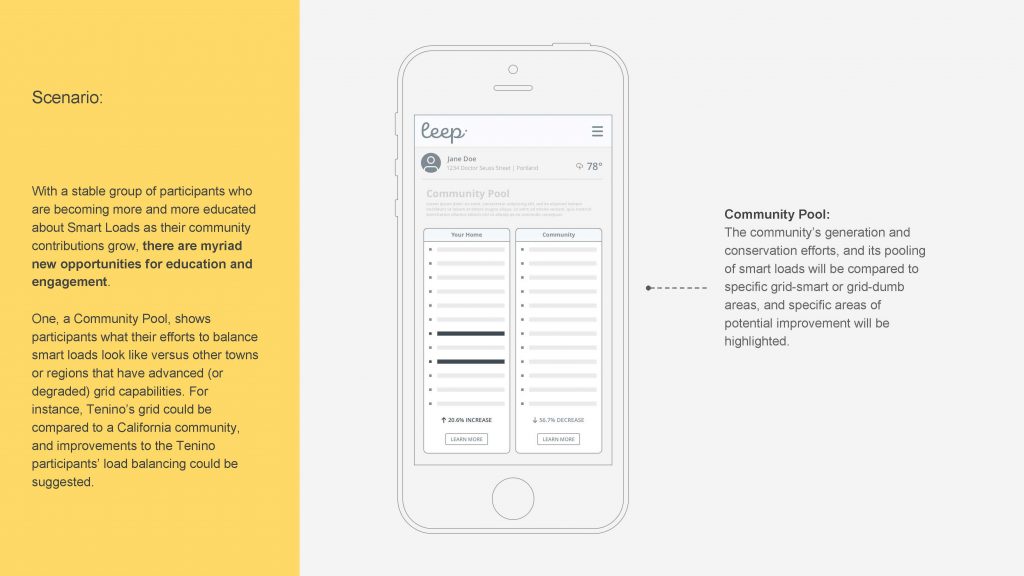
LEEP is designed as an interactive and intuitive way for families to engage proactively in managing their energy usage, saving money and enabling greater integration of clean energy technologies such as electric vehicles and renewable energy into the electrical grid.